- Private & confidential service
- Genuine medication
- All-inclusive service - No hidden fees
- Next day delivery
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Start your consultation
- Easy-to-use treatment
- Relief from uncomfortable IBS symptoms
- Combats diarrhoea and constipation
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a chronic condition that affects the digestive tract. Suffers can expect to experience recurrent episodes of diarrhoea and constipation as well as cramps and pain.
Learn more about the triggers and treatments of the condition and place your order below.
Topics
What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome?
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is an uncomfortable condition in which an individual suffers from symptoms of the digestive tract, especially the large intestine. It is generally chronic with cases ranging from mild to severe.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for the condition. However, a combination of medications and dietary and lifestyle changes can reduce the severity of symptoms. As the causes of IBS vary between individuals, over time you may discover certain triggers that can be managed and avoided.
If you have not been diagnosed with IBS, and experience sudden changes to your bowel movements or any unexplained sensation or discomfort, please contact your doctor - they will want to rule out more serious underlying causes, such as coeliac disease and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
What causes IBS?
Despite the condition being relatively common (one in five people will experience it at some point in their life), the exact cause of IBS is still unknown.
There are, however, several contributing factors that have been identified - these are individual to each patient.
Interestingly, IBS is more prevalent for those in their 20s and 30s. It is rare for it to present after someone is in their 50s. It also occurs more frequently in women, with twice as many developing the condition as men.
It is believed that IBS is caused by:
- an overly sensitive immune system or digestive tract - your body may react adversely to certain foods, particularly dairy products and carbonated drinks
- infection - some cases of IBS can first present after the patient has first suffered a serious stomach infection
- abnormal intestinal contractions - the muscles in your stomach and the walls of your intestine may be prone to over-contracting (causing diarrhoea and cramps) or contracting weakly (causing bloating and constipation)
- genetics - individuals with a family history of IBS are at an increased risk of developing the condition
If you do suffer from IBS, you will discover triggers that exacerbate symptoms. These are not causes of the condition, however, they may be responsible for more severe episodes of cramping, constipation and diarrhoea. The most commonly reported are:
- stress and anxiety
- hormones (especially when menstruating)
- foods (especially dairy products, alcohol and acidic/carbonated drinks)
If you are unsure about the triggers of your condition, you should consult a nutritionist or dietician. They will be able to help you identify difficult to digest foods in your diet. You should also consider counselling, to reduce any stress in your life.
What are the symptoms of IBS?
Everyone suffers from IBS differently, however, you can expect to experience one or more of the following:
- cramps
- abdominal pain
- bloating and gas
- constipation
- diarrhoea
It is also possible for chronic diarrhoea and constipation to cause other issues, such as haemorrhoids and rectal bleeding. If you experience either of these, you should consult your doctor for additional treatment.
Some of the above symptoms may also be signs of other serious conditions (such as colon cancer), which is why it is important to first be diagnosed with IBS by a doctor.
What treatments are available?
Thankfully, IBS does not pose a serious risk to your health, and despite the source of symptoms, alone it does not increase the risk of cancer or other bowel-related conditions.
Medications are focussed on dealing with whatever symptoms affect you most strongly. For some people, this may mean pain management.
There is no single treatment for IBS. Depending on what symptoms are most prevalent for you, will determine what medication is prescribed:
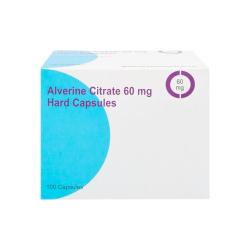
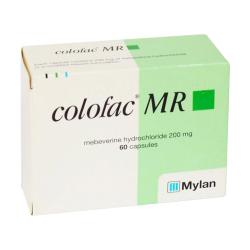
- antispasmodics - these are prescribed if you suffer from cramps and pain. They stop the intestine from contracting strongly and unexpectedly. HealthExpress sells the antispasmodics Colofac and Alverine
- laxatives - these are used to relieve constipation
- antidiarrheal - as the name suggests, these medications harden stools and reduce the severity of diarrhoea
Alternatively, if the medication does not have any effect over an extended period (normally 12 months), your doctor may advise psychological treatment:
- counselling or psychotherapy
- cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT)
- hypnotherapy
Though these treatment options may seem unrelated to the condition, as previously mentioned, stress and anxiety play a contributing role in the severity of IBS. Psychological methods can help you deal with symptoms and identify and limit symptom-inducing thoughts.
What are some health tips?
A significant factor in the severity of IBS is your diet. You should always consult with a dietician or doctor before making any radical or long-term changes to your diet, however, increasing fibre-intake is considered a sensible first step.
You should also consider keeping a food diary to identify any foods your body is intolerant towards.
You may find taking time to relax daily will have a considerable improvement to your condition - meditation is a good method of achieving this.
Likewise, regular exercise can help with reducing stress and also aids digestion.
3 simple steps to get you started